Catalog
Brooklyn provides a catalog, which is a persisted collection of versioned blueprints. These can be deployed directly or referenced by other blueprints. Blueprints in the catalog can be deployed via the Brooklyn REST API, or from the web-console’s “Catalog” tab of the “Create Application” wizard dialog box.
Catalog Items
An item to be added to the catalog is defined in YAML. This follows the syntax of a
YAML blueprint with an addition brooklyn.catalog section giving
the metadata needed to register the blueprint in the catalog:
brooklyn.catalog:
id: my-MySQL
version: 1.0
iconUrl: classpath://mysql.png
description: MySql is an open source relational database management system (RDBMS)
libraries:
- url: http://example.com/path/to/my-dependency-1.2.3.jar
- url: http://example.com/path/to/my-other-dependency-4.5.6.jar
services:
- type: brooklyn.entity.database.mysql.MySqlNodeTo explain the brooklyn.catalog fields:
- The
id: MySQLline specifies a unique ID used by Brooklyn to identify the catalog item. Other blueprints can reference the catalog item using this id. - The
version: 1.0line provides a unique version for the blueprint. Note that this is typically not the version of the software being installed (in this case MySQL). - The
iconUrl: classpath://...is an optional line where an icon can be specified for use with the item (in the “Add Application” dialog and elsewhere). Note thatclasspathURLs cannot refer to items in the OSGi bundle (to prevent requiring all OSGi bundles to be loaded at launch); use the server supplying the OSGi bundles or theconffolder of the Brooklyn distro instead. - The
description: ...line, also optional, allows supplying a free-format description of the blueprint.
The libraries section references OSGi bundles required for the blueprint. It can be omitted if everything
required by the blueprint is already on the Brooklyn classpath.
These URL’s should be to stable OSGi bundles;
if the contents at any of these URLs changes, the behaviour of the blueprint may change
whenever a bundle is reloaded in a Brooklyn server,
and if entities have been deployed against that version, their behavior may change in subtle or potentially incompatible ways.
To avoid this situation, it is highly recommended to use OSGi version stamps as part of the URL.
To reference a catalog item in another blueprint, simply reference its ID and optionally its version number. For example:
services:
- type: my-MySQL:1.0Adding to the Catalog
To add a catalog item to the catalog, POST the YAML file to /v1/catalog endpoint in
Brooklyn’s REST API.
To do this using curl:
curl http://127.0.0.1:8081/v1/catalog --data-binary @/path/to/mysql-catalog.yamlDeleting from the Catalog
You can delete a versioned item from the catalog using the same endpoint at the REST API.
For example, to delete the item with id my-MySQL and version 1.0 with curl:
curl -X DELETE http://127.0.0.1:8081/v1/catalog/entities/MySQL/1.0Note: Catalog items should not be deleted if there are running apps which were created using the same item. During rebinding the catalog item is used to reconstruct the entity.
Versioning
Version numbers follow the OSGi convention. This can have a major, minor, micro and qualifier part.
For example, 1.0. 1.0.1 or 1.0.1-20150101.
The combination of id:version strings must be unique across the catalog.
It is an error to deploy the same version of an existing item:
to update a blueprint, it is recommended to increase its version number;
alternatively in some cases it is permitted to delete an id:version instance
and then re-deploy.
If no version is specified, re-deploying will automatically
increment an internal version number for the catalog item.
When referencing a blueprint, if a version number is not specified the latest non-snapshot version will be loaded when an entity is instantiated.
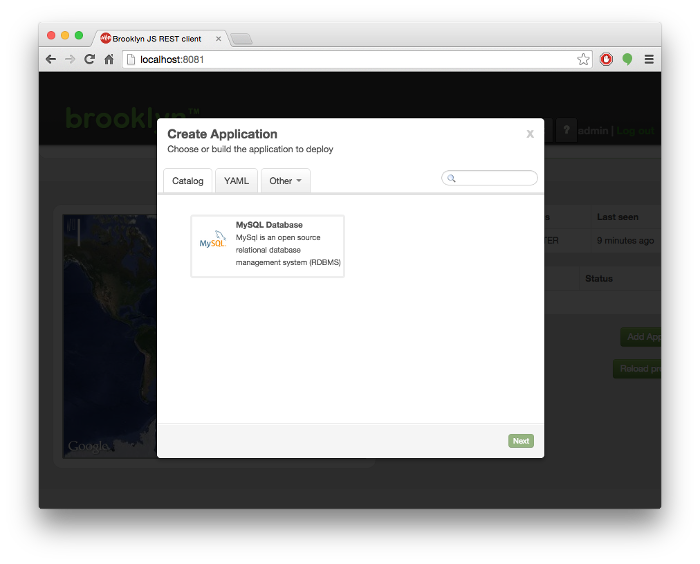
Special Requirements for the “Create Application” Wizard Dialog
For a blueprint in the catalog to be accessible via the ‘Create Application’ dialog, it must be an Application
(i.e. the entity at the root of the blueprint must implement brooklyn.entity.Application).
In contrast, if a YAML blueprint is deployed direct via the REST API, then this is not necessary.
For example, the MySql catalog item defined previously could be re-written to use a
brooklyn.entity.basic.BasicApplication, because no application-specific logic is
required other than to pass-through the start and stop commands.
the MySqlNode is added as a child of the BasicApplication.
brooklyn.catalog:
id: my-MySQL
version: 1.0
iconUrl: classpath://mysql.png
description: MySql is an open source relational database management system (RDBMS)
name: MySQL Database
services:
- type: brooklyn.entity.basic.BasicApplication
brooklyn.children:
- type: brooklyn.entity.database.mysql.MySqlNodeWhen added to the catalog via the HTTP POST command, the blueprint will appear in the ‘Create Application’ dialog
as shown here:
When deploying a new version of a blueprint, the catalog will show both the previous and the new versions of the blueprint. You may wish to delete the older version, assuming no applications currently running are using that old version.